Entering edit mode
2.3 years ago
donny.dw
▴
20
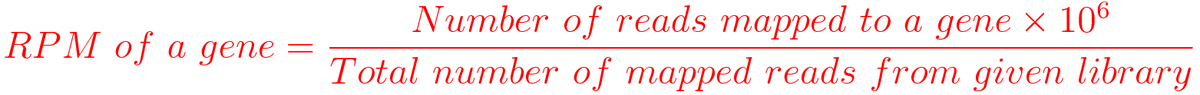
I am trying to understand RPM in ChIP-seq analysis. The definition of RPM is number of reads mapped mapped to a gene divide Total mapped reads. When I generate the bedgraph without "gene size", the values are too small.
scalingFactor = 1000000 / mappedReads
bedtools genomecov -ibam input.bam -bg - scale scalingFactor -g chrom.sizes > output.bedGraph
chr1 17441 17450 0.0621333
chr1 17450 17451 0.124267
chr1 17451 17592 0.1864
chr1 17592 17597 0.124267
chr1 17597 17602 0.0621333
chr1 139719 139766 0.0621333
chr1 139766 139870 0.124267
chr1 139870 139917 0.0621333
chr1 181344 181443 0.0621333
Do I need multiply some value to get RPM? What is the "gene size" I should use? 1000 or 10000?


ChIP-seq has no metric "gene size". That is something from RNA-seq if you want to correct for the fact that longer genes get more counts. It is not relevant in ChIP-seq, and in general RPM is outdated and performs poorly. Use this approach
=> ATAC-seq sample normalization (same applies to ChIP-seq)
here is why RPM is bad:
=> TMM-Normalization